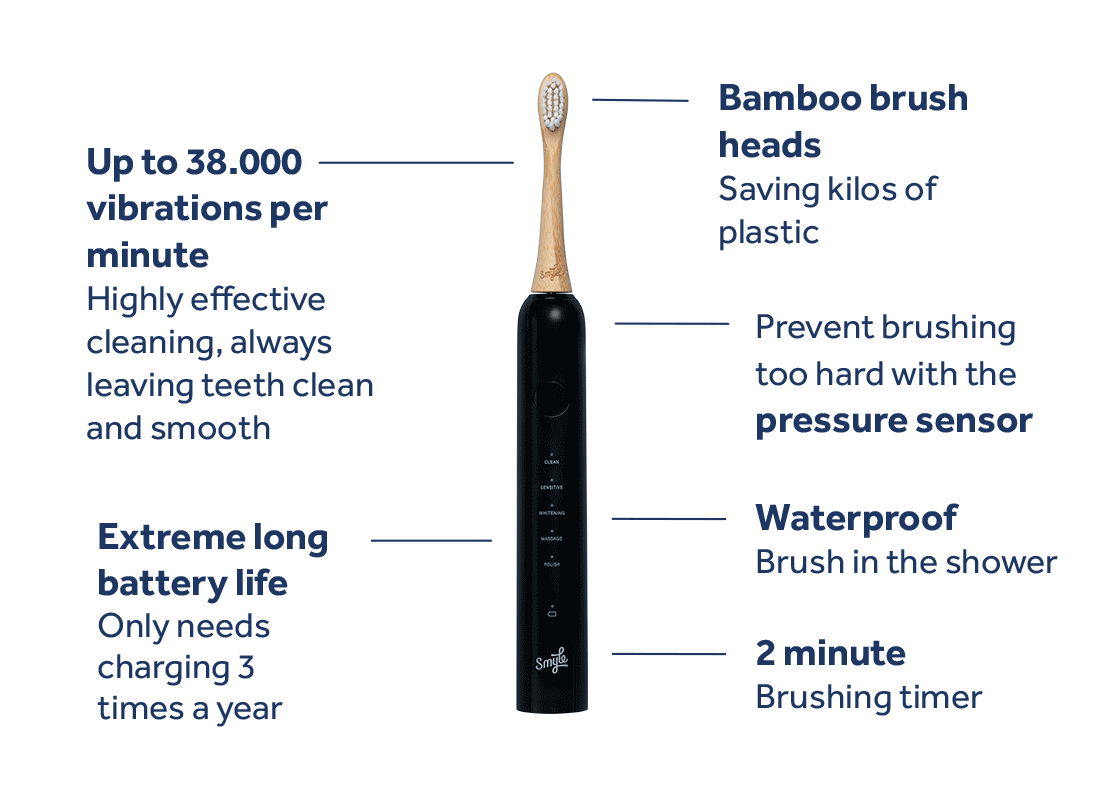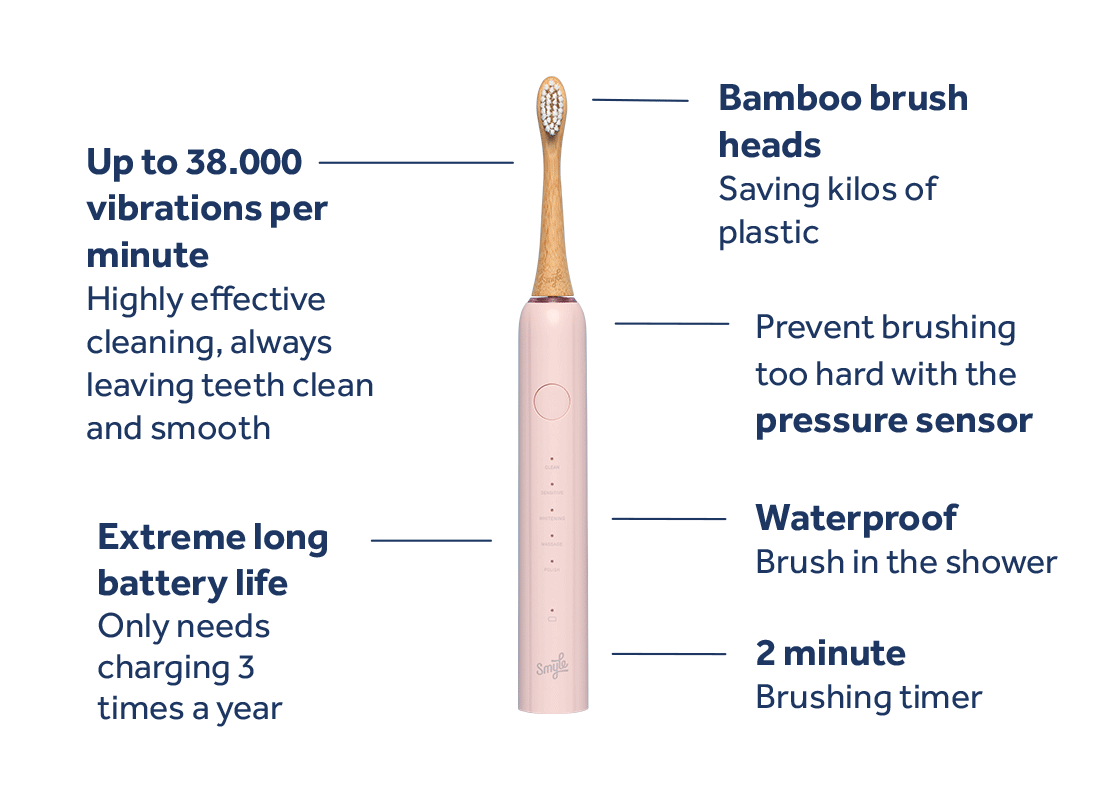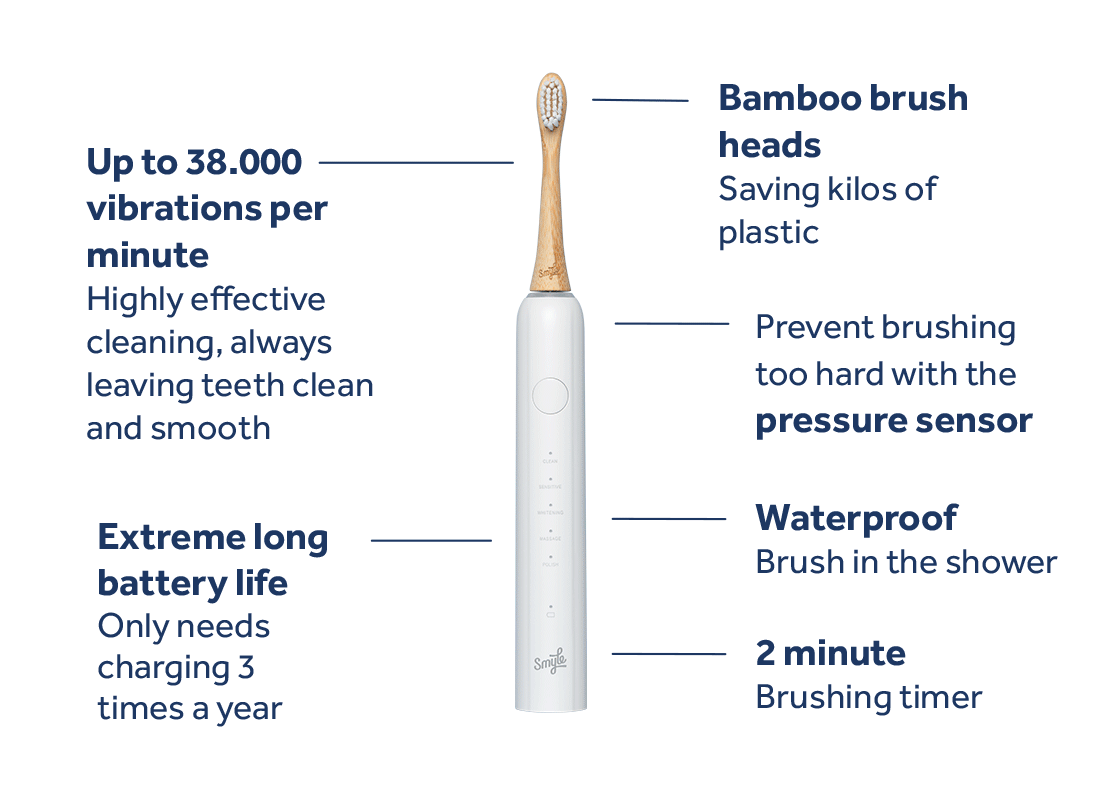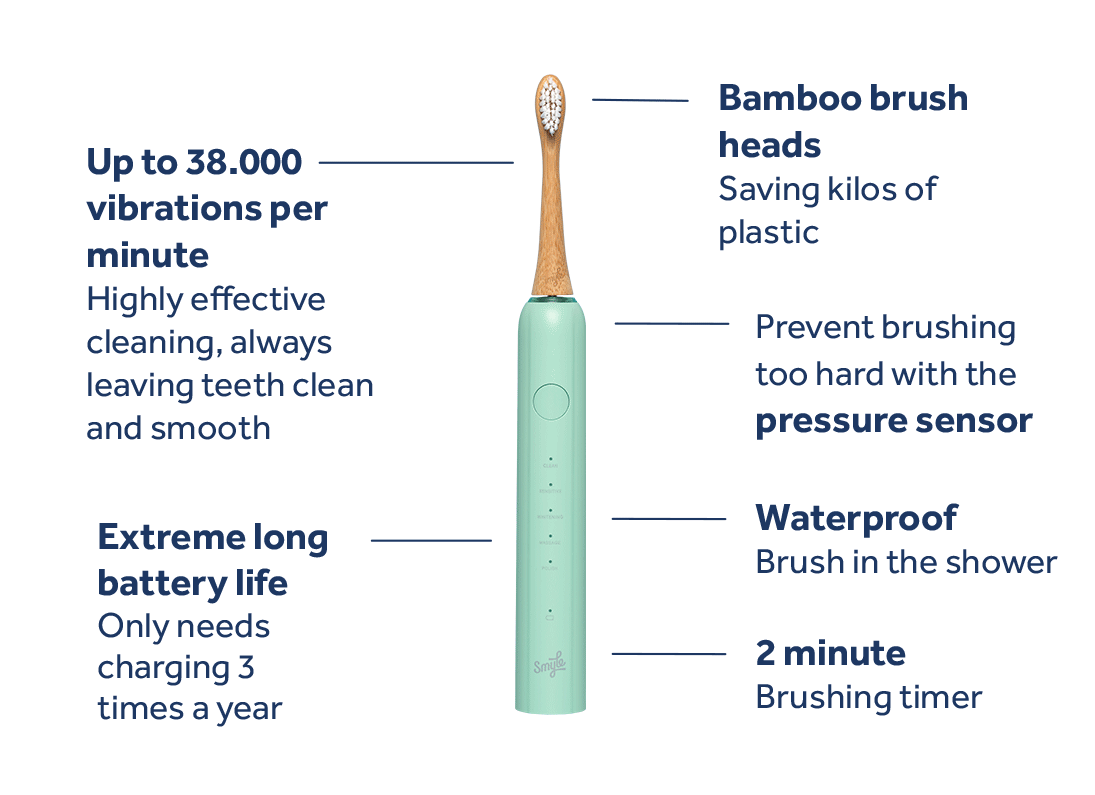
You may have heard of periodontitis—a serious gum disease that can significantly impact your oral health. That’s why it’s important to understand what it is, what causes it, and how to prevent it. We're here to guide you through the world of oral care, so you can keep your smile healthy the right way.
What Is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is a severe condition caused by several factors, with the primary cause being bacterial buildup in the mouth. Every day, a layer of plaque forms on your teeth—a mixture of bacteria, food particles, and saliva. If not removed properly through good oral hygiene, this plaque can harden into tartar, which creates an ideal breeding ground for bacteria.
These bacteria produce harmful substances that irritate the gums and cause inflammation. This inflammation is your immune system’s response to the infection. As a result, gums may become red, swollen, tender, and may bleed while brushing or flossing. If not treated early, the infection can spread deeper, damaging the gums, jawbone, and connective tissue that hold your teeth in place.
While bacteria are the main culprit, other factors can increase your risk, such as smoking, which weakens the body’s immune response and slows down healing.
Periodontitis has multiple stages—from mild (gingivitis) to advanced. In early stages, symptoms include gum inflammation and bleeding. If untreated, pockets form between the teeth and gums, trapping more bacteria and causing further damage. Eventually, the condition can spread to the jawbone, leading to loose or lost teeth.
Symptoms of Periodontitis
-
Gum problems: Redness, swelling, tenderness, and bleeding while brushing or flossing.
-
Bad breath (halitosis): Caused by bacteria thriving in the infected gum pockets.
-
Tooth loss: Advanced periodontitis damages the jawbone, loosening teeth until they fall out.
-
Changes in bite or chewing ability: Due to gum and bone damage.
Taking these symptoms seriously and acting early can help prevent long-term damage.
The Impact on Your Teeth and Overall Health
Periodontitis doesn’t just affect your mouth—it can have far-reaching consequences:
-
Tooth decay and loss due to weakened tooth support.
-
Difficulty chewing or speaking caused by pain or structural damage.
-
Aesthetic concerns like gum recession, tooth shifting, and facial changes that can affect self-confidence.
Health Risks Associated with Periodontitis
Periodontitis is also linked to several systemic health issues, including:
-
Heart disease: Inflammation from gum disease can enter the bloodstream, contributing to blood vessel damage, clots, and increased risk of heart attack or stroke.
-
Diabetes: People with diabetes are more prone to infections like gum disease, which in turn can make blood sugar harder to control.
-
Pregnancy complications: Gum inflammation can increase the risk of preterm birth, low birth weight, and other issues affecting both mother and baby.
This underlines the importance of early prevention and treatment to protect your health beyond the mouth.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Dentists diagnose periodontitis through a thorough oral exam, checking gum health and bone levels. Treatment may include:
-
Professional cleaning: Removes plaque and tartar to reduce inflammation.
-
Scaling and root planing: Deep cleaning under the gumline.
-
Surgical treatments (in severe cases): Such as flap surgery, bone grafts, or regenerative procedures.
Early treatment can prevent permanent damage and restore gum health. Regular dental checkups and prompt attention to symptoms like bleeding gums or persistent bad breath are key.
How to Prevent Periodontitis
You can prevent periodontitis by practicing the following:
-
Maintain good oral hygiene: Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss or use interdental brushes.
-
Visit your dentist regularly: Ideally every six months for early detection.
-
Eat a healthy diet: Avoid excess sugar; eat fiber-rich foods, fruits, and vegetables.
-
Manage stress: High stress levels can worsen gum health.
-
Quit smoking: Smoking severely increases your risk of gum disease and slows healing.
The Dentist’s Role Is Crucial
Dentists play a vital role in managing periodontitis by:
-
Providing deep cleanings to remove tartar and smooth tooth surfaces.
-
Offering guidance on brushing, flossing, and oral care products.
-
Tracking progress and preventing relapse through regular checkups.
With the support of your dental team, you can reduce the impact of periodontitis and restore your oral health.
Working Together Toward a Healthy Mouth
Periodontitis significantly affects your teeth, gums, and overall well-being. If left untreated, it can cause pain, tooth loss, functional issues, and even raise your risk for heart disease, diabetes, and pregnancy complications.
Regular dental visits and a strong oral care routine are your best defense. Through early detection, consistent care, and lifestyle changes, you can prevent periodontitis and keep your smile healthy for years to come.
Let’s work together toward better oral health—and a healthier life!